inset
inset(kwargs...)Manage figure inset setup and completion
The inset module is used to carve out a sub-region of the current plot canvas and restrict further plotting to that section of the canvas. The inset setup is started with the inset(...) directive that defines the placement and size of the inset. Subsequent plot commands will be directed to that window. The inset is completed via the inset(:end) directive, which reverts operations to the full canvas and restores the plot region and map projection that was in effect prior to the setup of the inset.
Description
The inset(...) defines the dimension and placement of the inset canvas. It records the current region and projection so that we may return to the initial plot environment when the inset is completed. The user may select any plot region and projection once plotting in the inset, but if the first command uses a projection that leaves off the scale or width then we supply a scale or width to fill the inset as best as possible, given the inset size and margins (if selected). Note: If you wish to let the inset dimensions be determined by the region and projection that will be used to draw in the inset, then give these arguments in the inset() command.
Required Arguments
D or pos or positionor inset_box or insetbox : – position=(map=true, inside=true, outside=true, norm=true, paper=true, anchor=XX, size=XX, width=XX, justify=code, offset=XX)
Define the map inset rectangle on the map. Specify the rectangle in one of three ways:
1. Use map=(lon,lat) for map coordinates. Requires both **region** and **proj** to be set.
2. Use inside=code or outside=code for setting the refpoint via a 2-char justification code that refers to
the (invisible) projected map bounding box. Requires both **region** and **proj** to be set.
3. Use norm=(x,y) for normalized bounding box coordinates (0-1). Requires both **region** and **proj** to be set.
4. Use paper=(x,y) for plot coordinates (append cm, inch, or point).
Use **size=(length,width)** (or **width**) of bounding rectangle or box in plot coordinates (inches, cm, etc.).
By default, the anchor point on the scale is assumed to be the bottom left corner (BL), but this can be changed
by using **justify=??** where *??* stands for a 2-char justification code *justify* (see text).
Note: with the default **outside=true**, the *justify* defaults to the same as **anchor**, if **inside=true** is used then *justify* defaults to the mirror opposite of **anchor**. Specify inset box attributes via the **box** option [outline only].
Alternatively, use **position="west/east/south/north"** of geographic rectangle bounded by parallels and
meridians; append **+r** if the coordinates instead are the lower left and upper right corners of the desired
rectangle. (Or, give *xmin/xmax/ymin/ymax* of bounding rectangle in projected coordinates and optionally
append **+u**unit [Default coordinate unit is meter (e)]. NOTE that this form requires passing the options
as a string and it uses the terse pure GMT syntax.
Optional Arguments
C or clearance : – clearance=val | clearance=(left=val, right=val, bott=val, bottom=val, top=val))
Reserve a space of dimension clearance between the actual inset plot area and the given inset box on the specified side, using side values from left=val, right=val, bottom=val, or top=val, or lr=val for both left and right or tb=val for both top and bott. No side means all sides. Alternatively, if all sides are to be set you can also give a pair of values separated by slashes (for setting separate horizontal and vertical margins), or the full set of four separate margins. Such space will be left untouched by the inset map plotting. Append units as desired (cm, inch, or point) [Default is set byPROJ_LENGTH_UNIT].
F or box : – box=(clearance=val, fill=color, inner=true, pen=pen, rounded=true, shaded=XX)
Without further options, draws a rectangular border around the map inset usingMAP_FRAME_PEN. The following modifiers can be appended to |-F|, with additional explanation and examples provided in the The background panel cookbook section:
- **clearance=val** where *val* is either *gap* or *(xgap,ygap)*, or *(lgap,rgap,bgap,tgap)* where these items are uniform, separate in x- and y-direction, or individual side spacings between the map embellishment and the border for each side.
- **fill=color**, where *color* is any valid color setting (see myreflink{Setting color}), to fill the scale panel [no fill].
- **inner=true** to draw a secondary, inner border as well. We use a uniform *gap* between borders of *2p* and the MAP_DEFAULTS_PEN unless other values are specified (like **inner="gap/pen"**).
- **pen=pen**, to specify different myreflink{Pen attributes} attributes.
- **rounded=true** to draw rounded rectangular borders instead, with a *6p* corner radius. You can override this radius by using another value instead of *true*.
- **shadded=true** or **shadded=(dx,dy)** or **shadded=shade** to draw an offset background shaded region. Here, *dx/dy* indicates the shift relative to the foreground frame [*4p/-4p*]and *shade* sets the fill style to use for shading ("gray50").
J or proj or projection : – proj=<parameters>
Select map projection. More at proj
N or noclip or no_clip : noclip=true
Do not clip features extruding outside map inset boundaries [Default will clip].
R or region or limits : – limits=(xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax) | limits=(BB=(xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax),) | limits=(LLUR=(xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax),units="unit") | ...more
Specify the region of interest. More at limits. For perspective view view, optionally add zmin,zmax. This option may be used to indicate the range used for the 3-D axes. You may ask for a larger w/e/s/n region to have more room between the image and the axes.
V or verbose : – verbose=true | verbose=level
Select verbosity level. More at verbose
Synopsis (end mode)
The inset(:end) command finalizes the current inset, which returns the plotting environment to the state prior to the start of the inset. The previous region and map projection will be in effect going forward.
The nested call mode
The options described above respect the pure use of inset as a modern mode function. But we can also use it in a mix mode in one-liners commands. It is mixed because the functioning relies in mixing the classic and modern modes (in a way transparent to the user). And, as just said, this mix mode consists in calling the inset function as an option to the plot, basemap and grdimage functions. Since we are doing a nested call, we need to pass all options as argument to inset and this ofc reduces the number of possibilities but still, it offers quite nice features that allow creating elaborated figures with very short commands. The Figure insets shows several examples of this usage.
The inset windows are located according to an algorithm that tries to avoid overlapping lines in line plots (with a moderate success), or in some corner position for insets with images. Inset windows sizes are also automatically estimated from image sizes and projections (when they are geographical). However, user can manually control this wth position option explained above.
inset – inset=(data, zoom=(...), coast=(...), position=(...), box=(...), clearance=(...))
- **data** An image, a grid a table (GMTdataset) or a file name that can be automatically read by gmtread. Depending on the data type an _x,y_ plot or an image is displayed inside the inset window.
- **zoom** This refers to an area of the main window that we wish to make a zoom of. Its arguments depend
on whether we are zooming an _x,y_ plot or an image. In the first case we pass an _x_ location and a half-width.
For example zoom=(10,2) means that the zoom window covers the abscissa [8 12] range. The _y_ extent is whatever
the line has between those _x_ limits. But for the case of images we need one more argument because now we have 2
dimensions. The syntax now is zoom=(x0,y0,delta), an extension of the previous concept, which requires that the
units of _x_ and _y_ are the same and we get a square zoom window. The alternative is to use the usual way of GMT
specifying region limits. That is zoom=(x_min, x_max, y_min, y_max)
- **pzoom** When adding insets to images we can provide an external image (or file name) that will be displayed
in the inset. But since in this case the inset does not have to share the same coordinates with main figure, we
only provide here the point coordinates of the interesting area. The syntax is hence pzoom=(x0,y0).
- **coast** With this argument we can call the coast command with all of its normal arguments. And
furthermore, we can even call the plot (or any of its avatars) to add line/symbol plots over the
inset map. A further option to this form of calling coast is the option rect=?. If ? is true, it will
plot a 0.75 pt blue rectangle showing the main window limits. Alternatives is rect=number, rect=color or rect=(number, color), where color is a color name and number is the rectangle line thickness in points
- **position, box, clearance** Have the same meaning/usage as explained above.
Examples
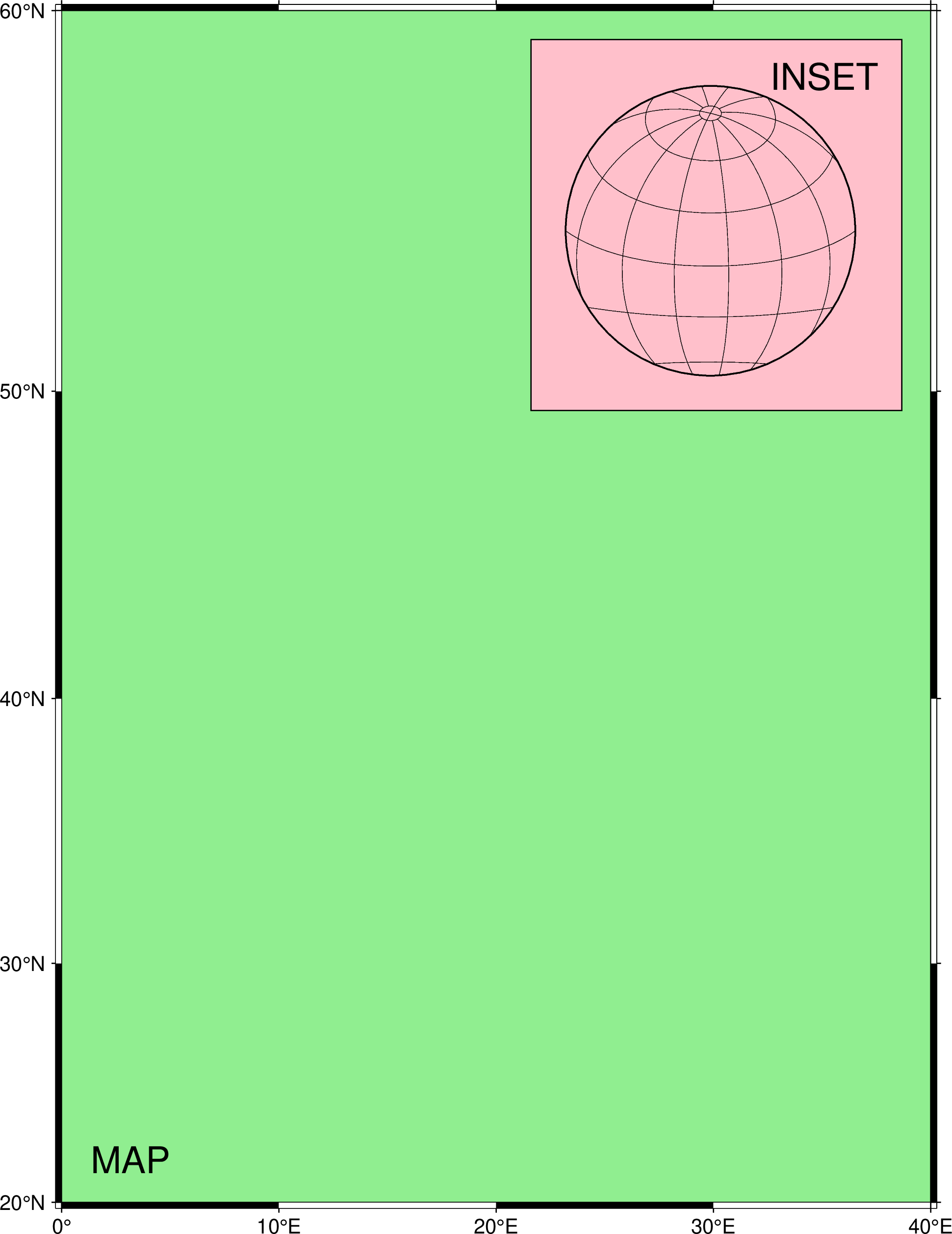
To make a simple basemap plot that demonstrates the inset module, try
using GMT
gmtbegin()
basemap(region=(0,40,20,60), proj=:merc, frame=(annot=:afg, fill=:lightgreen))
inset(position=(anchor=:TR, width=6.4, offset=0.5), box=(fill=:pink, pen=0.5), margins=0.6)
basemap(region=:global360, proj=(name=:laea, center=[20,20]), figsize=5, frame=:afg)
text(text="INSET", font=18, region_justify=:TR, offset=(away=true, shift=-0.4), noclip=true)
inset(:end)
text(text="MAP", font=18, region_justify=:BL, offset=(away=true, shift=0.5))
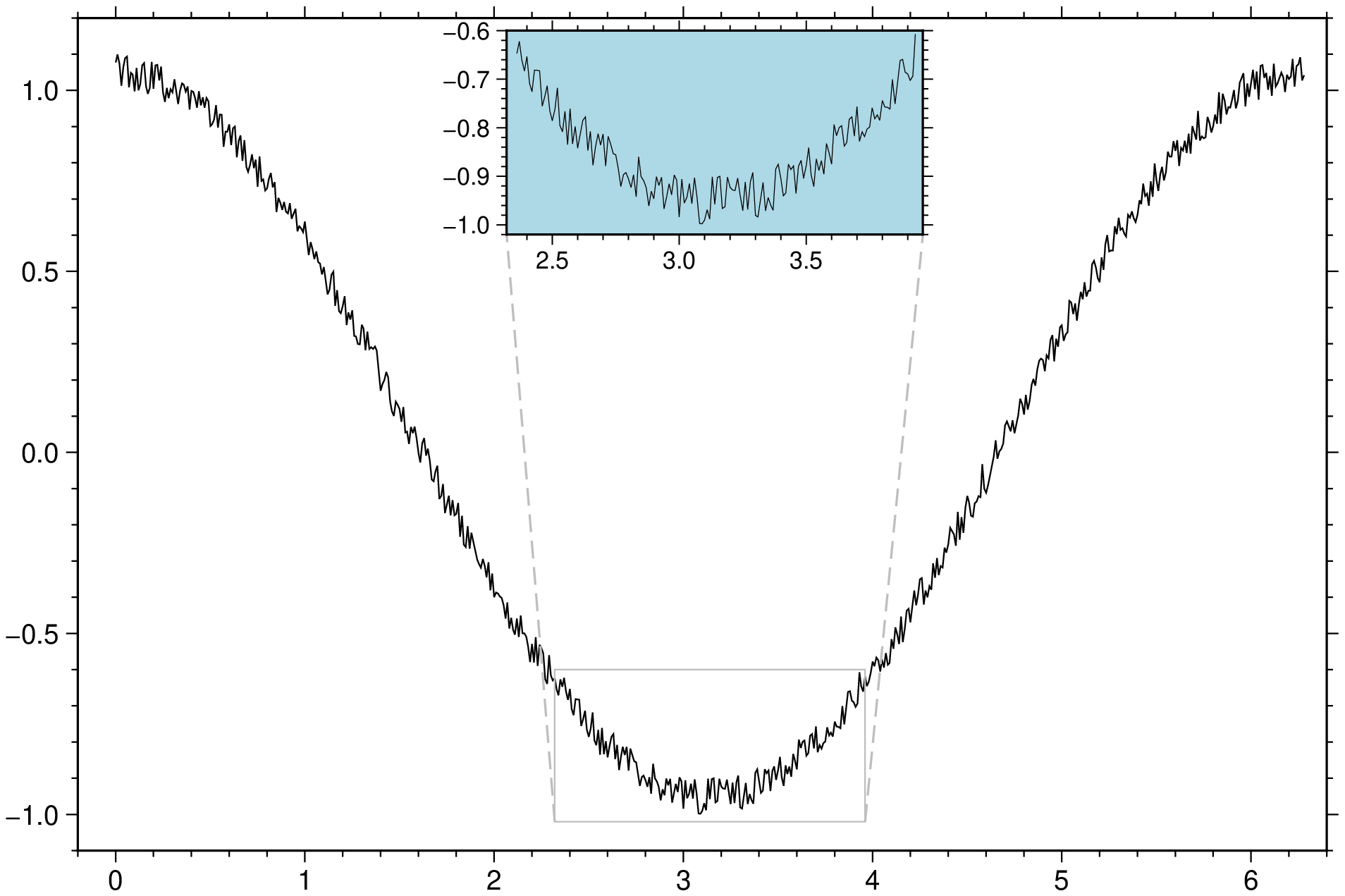
gmtend(:show)Make a zoom over a region of a synthetic plot.
using GMT
t = 0:0.01:2pi;
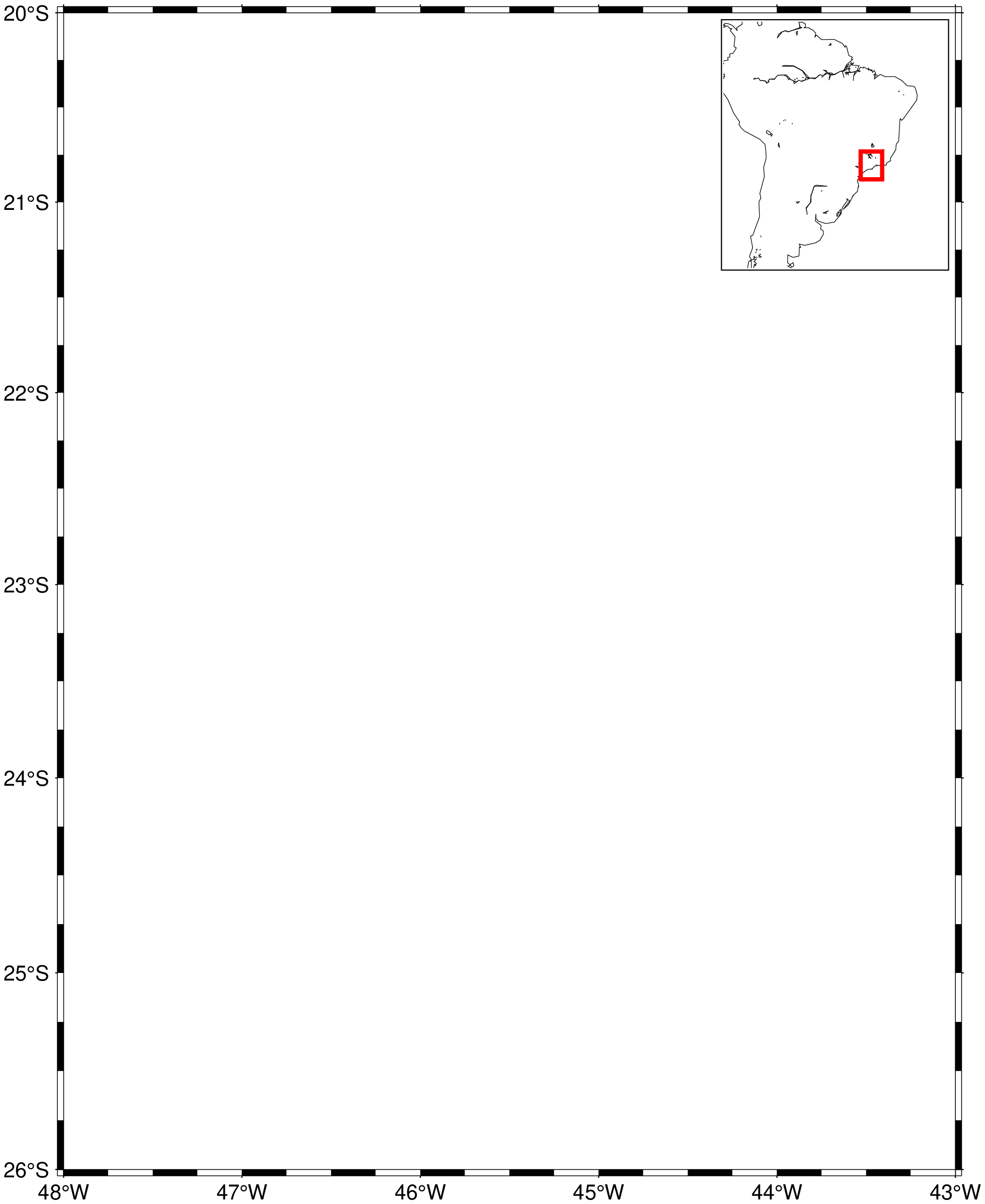
plot(t, cos.(t).+rand(length(t))*0.1, inset=(zoom=(pi,pi/4), box=(fill=:lightblue,)), show=true)Add an inset to basemap image with a rectangle in the inset taken from main image limits.
using GMT
basemap(region=(-48,-43,-26,-20), proj=:merc,
inset=(coast, R="-80/-28/-43/10", proj=:merc, shore=true, rect=(2,:red)), show=true)These docs were autogenerated using GMT: v1.33.1